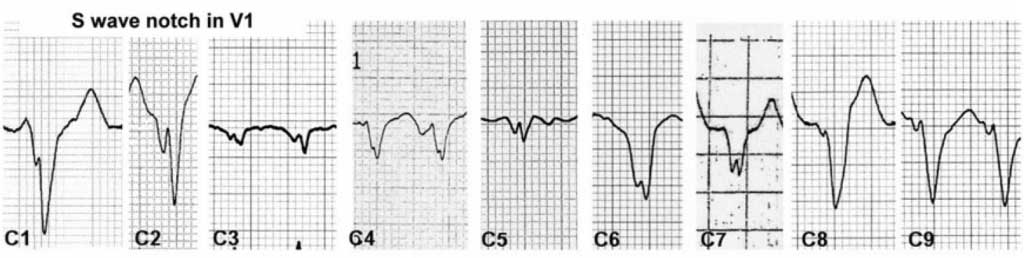
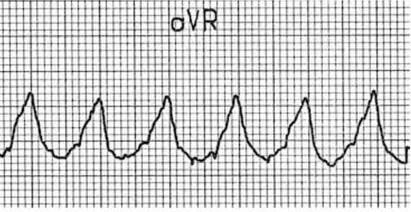
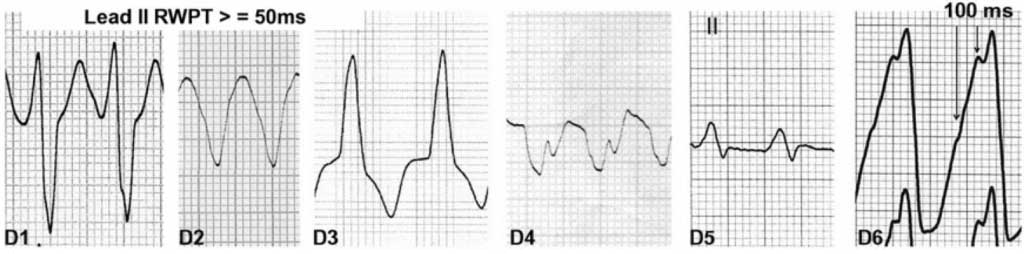
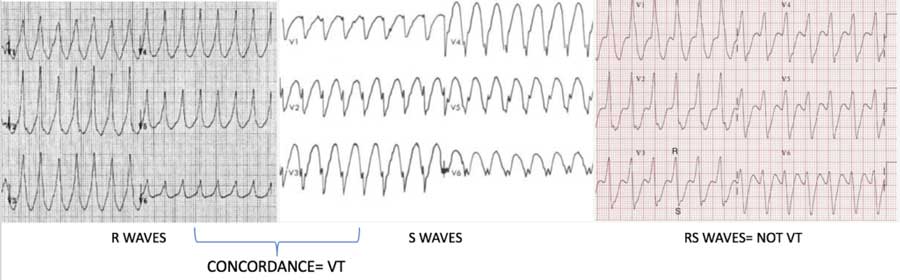
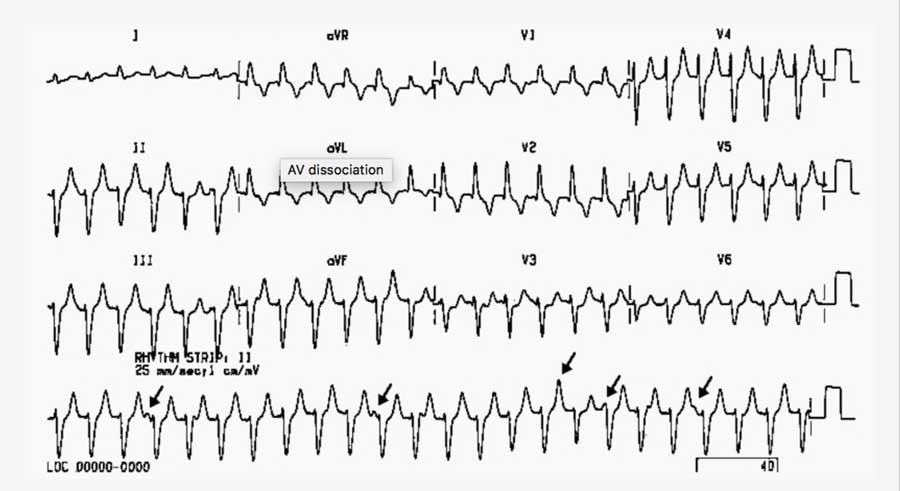
ECG OF THE WEEK
Each Week we put up one ECG case for you....because it's easier to learn from cases.
The ECG of the week is FREE to everyone. To become an expert at ECG's join the Cardiac Bootcamp Course. It's a great way to Learn!
Or come to one of our LIVE Cardiac Bootcamps
The ECG of the week is FREE to everyone. To become an expert at ECG's join the Cardiac Bootcamp Course. It's a great way to Learn!
Or come to one of our LIVE Cardiac Bootcamps